# Module
# 分割
將 store 分割成 module,每個 module 擁有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter。
const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
moduleA,
moduleB
}
})
store.state.moduleA // -> moduleA 的state狀態
store.state.moduleB // -> moduleB 的state狀態
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 作用域
module 內部的 mutation 和 getter,接收的第一個參數為 Module 作用域物件。
const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
// count 會寫到全域
// 取用方法: $store.state.moduleA.count
state: { count: 0 },
mutations: {
increment(state) {
// state: Module 作用域物件
state.count++;
},
},
getters: {
// 取用方法: $store.getters.moduleA.doubleCount
// 或: $store.rootGetters.doubleCount
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2;
},
},
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
action 同樣也是使用 Module 作用域物件。
const moduleA = {
// ...
actions: {
// state: 作用域狀態
// rootState: 根節點、子節點的 state 資料
// rootGetters: 根節點、子節點的 getters 資料
actionIncrement({ state, dispatch, commit, rootState, rootGetters }) {
if ((state.count + rootState.count) % 2 === 1) {
commit('increment');
}
},
},
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 命名空間
默認情況下,模組內部的 action、mutation 和 getter 是註冊在 全域 的命名空間。
這樣使得多個模組能夠對同一 mutation 或 action 作出響應。
通過添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成為帶命名空間的模組。
當模組被註冊後,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都會自動根據 模組註冊的路徑 調整命名。
# 範例
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
account: {
namespaced: true,
// 模組內容(module assets)
// 模組內的狀態已經是嵌套的了,使用 namespaced 屬性不會對其產生影響
state: { ... },
getters: {
isAdmin () { ... } // -> getters['account/isAdmin']
},
actions: {
login () { ... } // -> dispatch('account/login')
},
mutations: {
login () { ... } // -> commit('account/login')
},
// 嵌套模組
modules: {
// 繼承父模組的命名空間
myPage: {
state: { ... },
getters: {
profile () { ... } // -> getters['account/profile']
}
},
// 進一步嵌套命名空間
posts: {
namespaced: true,
state: { ... },
getters: {
popular () { ... } // -> getters['account/posts/popular']
}
}
}
}
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
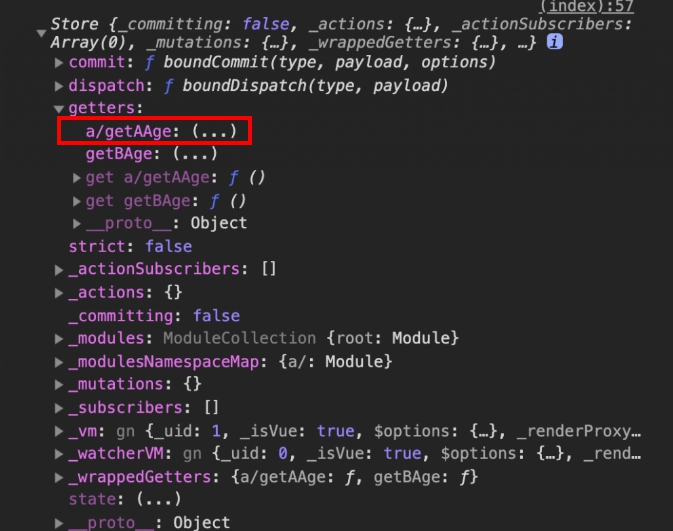
在 mapActions,mapMutations 與 mapGetters 中皆需也使用模組的註冊名稱作為呼叫的路徑。
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
export default {
name: 'MyComponent',
computed: {
...mapGetters({
getAAge: 'a/getAAge',
getBAge: 'getBAge',
}),
},
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 命名空間的綁定函數
使用 mapState、mapGetters、mapActions 和 mapMutations。
可以通過使用 createNamespacedHelpers 創建基於某個命名空間輔助函數。
可用於找 自身和其他模組 的
state
// 注意這一段
import { createNamespacedHelpers } from 'vuex';
const { mapState, mapActions } = createNamespacedHelpers('some/nested/module');
export default {
computed: {
// 在 `some/nested/module` 中查找
...mapState({
a: (state) => state.a,
b: (state) => state.b,
}),
...mapGetters({
getAAge: 'getAge',
}),
},
methods: {
// 在 `some/nested/module` 中查找
...mapActions(['foo', 'bar']),
},
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 第三個參數
在 namespaced: true 下,commit 和 dispatch 的第三個參數可以指定 { root: true },表示從 Vuex 根元件 呼叫一個方法,他可以根據 Module 的設定來 戳 到指定的目標。
store.commit('a/other/module', {}, { root: true });
store.dispatch('a/other/module', {}, { root: true });
2
使用情境:在本身的 Module 中,需要去呼叫其他 Module 的時候,必須要加上這個參數,這樣才能觸發到想要的目標。不然依照 namespaced: true 的設定,在 Module 裡面的 commit 都是觸發本地端 (Local state) 的方法 (包括 commit 或是 dispatch)。
所以,Module 是 namespaced: true 的話,第三個參數沒有設定,就會被回報錯誤。