# 物件、陣列與型別判斷
# 物件的擴充修改與調整
下面三種方法是針對物件本身做操作,但因物件有參考特性,無法對巢狀的屬性 有所動作。
# preventExtensions
中文語意:防止擴充
Object.preventExtensions(person);
// 驗證是否可被擴充
console.log('是否可被擴充', Object.isExtensible(person));
console.log(
'person a 的屬性特徵',
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(person, 'a')
);
// 調整屬性
person.a = 'a';
// 新增屬性
person.d = 'd';
// 巢狀屬性調整
person.c.a = 'ca';
// 調整特徵
Object.defineProperty(person, 'a', {
configurable: false,
});
// 刪除
delete person.b;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20

# seal
中文語意:封裝
- 物件屬性無法新增刪除,也無法重新配置特徵,但可以調整目前屬性值
- 預設物件會被加上
preventExtensions
Object.seal(person);
// 驗證是否可被擴充
console.log('是否可被擴充', Object.isExtensible(person));
// 驗證是否被封裝
console.log('是否被封裝', Object.isSeal(person));
console.log(
'person a 的屬性特徵',
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(person, 'a')
);
// 調整屬性
person.a = 'a';
// 新增屬性
person.d = 'd';
// 巢狀屬性調整
person.c.a = 'ca';
// 調整特徵
Object.defineProperty(person, 'a', {
writable: false,
});
// 刪除
delete person.b;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22

# freeze
中文語意:凍結
物件會加上 seal,並且無法調整值。
Object.freeze(person);
// 驗證是否可被擴充
console.log('是否可被擴充', Object.isExtensible(person));
// 驗證是否被封裝
console.log('是否被封裝', Object.isSeal(person));
// 驗證是否被凍結
console.log('是否被凍結', Object.isFrozen(person));
console.log(
'person a 的屬性特徵',
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(person, 'a')
);
// 調整屬性
person.a = 'a';
// 新增屬性
person.d = 'd';
// 巢狀屬性調整
person.c.a = 'ca';
// 調整特徵
Object.defineProperty(person, 'a', {
configurable: false,
});
// 刪除
delete person.b;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24

# 理解 JavaScript 建構式
由於函式也是個物件,所以可以借用來當作「建構式」來建立其他物件:
function Person(name, age, gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.greeting = function() {
console.log('Hello! My name is ' + this.name + '.');
};
}
const alex = new Person('Alex', 32, 'male');
alex.greeting(); // "Hello! My name is Alex."
const john = new Person('John', 10, 'male');
john.greeting(); // "Hello! My name is John."
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
像這樣,建立了一個 Person 建構式 (Constructor) ,然後可以就透過 new 關鍵字來建立各種對應的物件。
# 拆解透過 new 建立物件的流程
const alex = new Person('Alex', 32, 'male');
/*
===> const alex = {};
===> Person.call(alex, 'Alex', 32, 'male');
*/
2
3
4
5
6
透過 new Person(...) 這個動作,傳回的物件會有 name、age、gender 以及 greeting 屬性,而 JavaScript 會在背景執行 Person.call 方法,將 alex 作為 this 的參考物件,然後把這些屬性通通新增到 alex 物件中。
提醒
即使透過建構式建立的物件,這個物件的屬性仍然可以透過 . 來公開存取:
alex.age = 18;
# 物件屬性描述器
我們可以透過新的物件模型來控制物件屬性的存取、刪除、列舉等功能。這些特殊的屬性會將它們稱為 屬性描述器 (Property descriptor)。
屬性描述器一共可以分為六種:
value- 屬性的值writable- 屬性是否可以改變,如果是false那就是唯讀屬性enumerable- 物件內的屬性是否可以透過for-in語法來迭代configurable- 屬性是否可以被刪除、或修改屬性內的writable、enumerable及configurable設定get- 物件屬性的 getter functionset- 物件屬性的 setter function
上述除了 value 之外的值都可以不設定,writable、enumerable 及 configurable 的預設值是 true,而 get 與 set 如果沒有特別指定則是 undefined。
這些屬性描述器必須透過 ES5 所提供的 Object.defineProperty() 來處理。
# Object.defineProperty 和 Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor
我們可以透過 Object.defineProperty 來定義物件的屬性描述。
用法:Object.defineProperty(物件對象, 屬性, 屬性描述器)。
一般要建立一個簡單物件,可以用:
const person = {
name: 'alex',
};
2
3
另外,也可以透過 Object.defineProperty 來定義物件的屬性:
const person = {};
Object.defineProperty(person, 'name', {
value: 'alex',
});
2
3
4
5
接著可以用 Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor() 來檢查物件屬性描述器的狀態:
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(person, 'name');
// {
// configurable: false
// enumerable: false
// value: "alex"
// writable: false
// }
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
注意
透過 Object.defineProperty 定義物件屬性,預設的情況下,writable、enumerable 及 configurable 都是 false。
而透過物件實字方式建立的屬性,預設值則會是 true。
# 屬性的 get 和 set 方法
使用屬性的 get 和 set 有兩種方法。
利用 物件實字建立物件 的時候,即定義好
get和set的方法const wallet = { total: 100, get save() { return this.total / 2; }, set save(price) { return (this.total += price / 2); }, }; console.log(wallet.save, wallet); // 使用等號賦值,而非函式 wallet.save = 300;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13預設
save屬性為(...),當點開後,才會針對目前的total做getter取值利用
Object.defineProperty()定義const wallet = { total: 100; } // 預設的 save 屬性,configurable 和 enumerable 皆為 false Object.defineProperty(wallet, 'save', { // 可以選擇是否加回來 // configurable: true, // enumerable: true, get() { return this.total / 2; }, set(price) { return this.total += price / 2 } }) wallet.save = 300;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17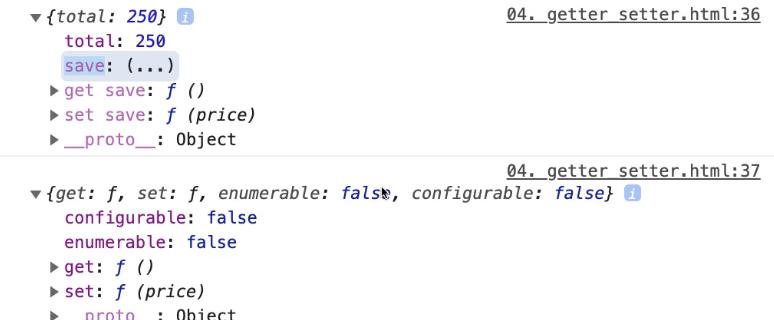
注意
如果定義了 get 和 set 的方法,表示要自行控制屬性的存取範圍,那麼就不能再去定義 value 或 writable 的屬性描述。
Object.defineProperty(person, 'firstName', {
value: 'firstName',
writable: true,
get: function() {
return this.name;
},
set: function(name) {
this.name = name;
},
});
// Uncaught TypeError: Invalid property descriptor.
// Cannot both specify accessors and a value or writable attribute, #<Object>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
使用 get 方法新增 Array 的原型方法:
const a = [1, 2, 3];
// 直接操作陣列原型
Object.defineProperty(Array.prototype, 'latest', {
get() {
return this[this.length - 1];
},
});
a.latest; // 3
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 陣列
陣列的長度可以由 array.length 來取得,而 length 屬性的值是 可以被覆寫 的:
const animals = ['cat', 'dog', 'bird'];
animals.length = 1;
console.log(animals); // ['cat']
animals.length = 3;
console.log(animals); // ['cat', undefined, undefined]
2
3
4
5
6
7
上面的例子中,陣列 animals 原本的長度為 3,後來透過 animals.length = 1; 設定成 1 之後,後面的元素就被移除了。
即使之後再度修改成 animals.length = 3;,後面的兩個元素也只會被 undefined 所填補。
# 如何判斷是否為陣列
可以使用 isArray() 方法:
Array.isArray([]); // true
Array.isArray([1]); // true
Array.isArray(new Array()); // true
2
3
# 型別判斷
若要在 JavaScript 中檢查變數型別,正確來說應該是 值的型別,變數沒有型別,值才有,可以透過 typeof 運算子來處理。
要注意的是,透過 typeof 運算子回傳的東西都是 字串。
# 為什麼函式的型別是 function 而不是 object?
當我們透過 typeof 去檢查一個「函式 (function) 」的時候,雖然會得到 "function" 的結果,誤以為 function 也是 JavaScript 定義的一種型別,但實際上它仍屬於 Object 的一種,可以把它想像成是一種可以被呼叫 (be invoked) 的特殊物件。
MDN 對
function的定義:Every JavaScript function is actually a
Functionobject.This can be seen with the code
(function(){}).constructor === Function, which returns true.
# Pass by sharing
當函式的參數被 整個 重新賦值的時候,外部變數的內容是不會被影響的。
const coin = { value: 10 };
const changeValue = (coin) => {
return (coin = { value: 123 });
};
changeValue(coin); // {value: 123}
console.log(coin); // {value: 10}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
但如果是 屬性 被重新賦值,則會發生改變:
const changeValue = (coin) => {
return (coin.value = 123);
};
changeValue(coin); // 123
console.log(coin); // {value: 123}
2
3
4
5
6